Geomorphic Assessments
Geomorphic assessments of the Touchet and Tucannon River basins help landowners and Columbia Conservation District staff make informed decisions about river restoration activities, identify potential project areas, and meet animal and habitat development goals as outlined by the district.

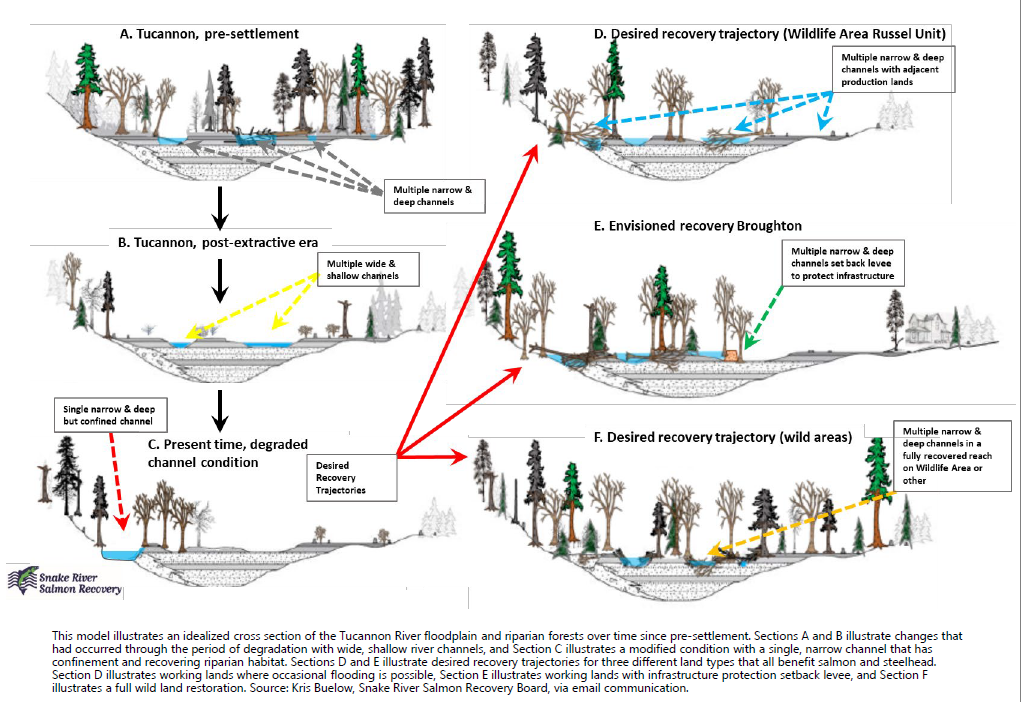
Image: This model illustrates an idealized cross section of the Tucannon River floodplain and riparian forests over time since pre-settlement. Sections A and B illustrate changes that had occurred through the period of degradation with wide, shallow river channels, and Section C illustrates a modified condition with a single, narrow channel that has confinement and recovering riparian habitat. Sections D and E illustrate desired recovery trajectories for three different land types that all benefit salmon and steelhead. Section D illustrates working lands where occasional flooding is possible, Section E illustrates working lands with infrastructure protection setback levee, and Section F illustrates a full wild land restoration.
Source: Kris Buelow, Snake River Salmon Recovery Board, via email communication.
Related Links
Related Questions
By using the data gathered in the geomorphic assessment as reference, CCD and its partners are able to zero in on good “project candidate areas”. Topographical and fluvial data help determine what restoration activities will have the best results depending on the goals of the landowner. Restoration activities that increase channeling and floodplain connectivity help reduce erosion and reduce the impacts of flooding by allowing water to pass through multiple channels reducing the overall energy potential as compared to a single channel stream.
The Touchet Basin is a good candidate for restoration activities for several strategic reasons. First is that restoration activities will have multifaceted benefits for the local area. The Touchet River is large enough to produce and provide habitat for a lot of fish, as well as providing recreational activities. The river is not so large that restoration treatments struggle to stay in place, restoration treatments are not too large in scale, and are not as costly to construct since projects don’t have to be as large.
- Floodplain Connectivity– the flow, exchange and pathways that move organisms, energy, and matter throughout a floodplain
- Measuring the existing connected floodplain as well as potential floodplain targets, and determine floodplain potential
- A connected, functional floodplain moderates the effects of floods and droughts on a river system by retaining water during periods of high flow and re- releasing it during periods of low flows.
- Channel Complexity– generally refers to heterogeneity of physical stream geometry or habitat
- By modeling river reaches at various flow conditions we are able to determine which areas of the river are complex and which are not
- Transport Capacity– the total amount of sediment a stream is able to transport
- Stream reaches that exhibit high transport capacity are often times incised,
- Gravel Augmentation Plan– Determine
- Gravel and other substrate materials are critical to aquatic organisms that live in rivers. Determining areas in the river basins where substrate is inadequate for fish and other aquatic organisms informs restoration activities.
